Genoa Italy travel guide: Embark on a captivating journey through the historical heart of Liguria. This guide unveils the hidden gems and vibrant energy of Genoa, a city steeped in maritime history and modern charm. From its iconic landmarks to its delicious cuisine, we’ll explore everything you need to know to plan an unforgettable trip.
Discover Genoa’s unique character, contrasting its rich past with its lively present. Explore the city’s historical evolution, from its maritime roots to its architectural wonders, and uncover the stories that shape its vibrant atmosphere.
Introduction to Genoa
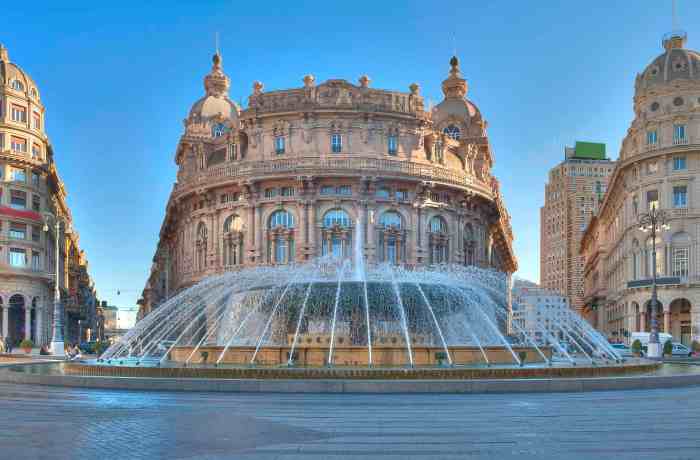
Genoa, a vibrant port city nestled on the Ligurian coast of Italy, boasts a rich tapestry woven from centuries of maritime trade, artistic innovation, and cultural exchange. Beyond its stunning coastal scenery, the city pulsates with a unique energy, a blend of old-world charm and modern dynamism that sets it apart from other Italian destinations. Its historical significance as a major maritime power has profoundly shaped its architecture, its cultural identity, and its enduring appeal.Genoa’s character is undeniably distinct.
Genoa, Italy, is a fantastic city for a trip, with its stunning architecture and delicious seafood. But if you’re looking for some great meat-free options while exploring, check out this helpful guide for finding tasty vegetarian and vegan eats in Amsterdam: meat free munching herbivores guide amsterdam. It’s a great resource for anyone wanting to discover the city’s diverse culinary scene, and hopefully you’ll find some inspiration for your own Genoese adventures.
Its narrow, winding streets, often lined with historic palazzi, whisper tales of a powerful past. The city’s maritime heritage is palpable in its architecture, from the impressive harbor to the opulent merchant houses. This unique blend of history and modernity makes Genoa a captivating destination for travelers seeking a deeper understanding of Italy’s diverse past.
Historical Significance
Genoa’s prominence as a major maritime power dates back to the 11th century. The Republic of Genoa, a powerful maritime republic, flourished during the Middle Ages, controlling vast trade routes across the Mediterranean. This period of expansion significantly impacted the city’s development, shaping its architecture, economy, and social structure. Genoese explorers and merchants ventured across the globe, establishing colonies and fostering cultural exchange.
Key figures like Christopher Columbus, though not exclusively Genoese, were part of the wider Genoese network of exploration and trade. This period left an indelible mark on the city, evident in the magnificent palazzi and intricate street layouts that still stand today.
Genoa’s Maritime History and Architecture
Genoa’s role as a major maritime power profoundly influenced its architecture. The city’s impressive harbor, a vital hub for trade and commerce, is a testament to its maritime past. Numerous palazzi, built by wealthy merchants and traders, reflect the opulence and grandeur of Genoa’s maritime trade. These structures, often adorned with intricate details and showcasing a unique blend of architectural styles, are a tangible link to the city’s history.
The city’s maritime tradition is evident in the construction of its buildings, from the imposing port facilities to the elegant houses lining the narrow streets.
Planning a trip to Genoa, Italy? Beyond the historical sites and stunning harbor views, discovering the best local eateries is key to experiencing the real heart of the city. For inspiration on finding incredible, locally-owned restaurants across the US, check out this helpful guide: best locally owned restaurants in united states. Ultimately, a true travel experience in Genoa involves immersing yourself in the local culinary scene.
Exploring these gems will undoubtedly enrich your Genoa travel memories.
Key Historical Dates and Events
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 1099 | Genoa forms a naval alliance with Pisa to combat the Saracens in the Mediterranean |
| 1155 | Genoa defeats Pisa at the Battle of Meloria, gaining dominance over the Western Mediterranean trade routes |
| 1258 | Genoa establishes its first colony in the Black Sea |
| 1350-1500 | Genoa experiences a period of prosperity and expansion, with the construction of numerous impressive palazzi |
| 1453 | The fall of Constantinople to the Ottomans shifts trade routes and impacts Genoa’s dominance |
This table provides a concise overview of key historical events that shaped Genoa’s development. Each event contributed to the city’s unique character and the architecture that defines it today.
Must-See Attractions
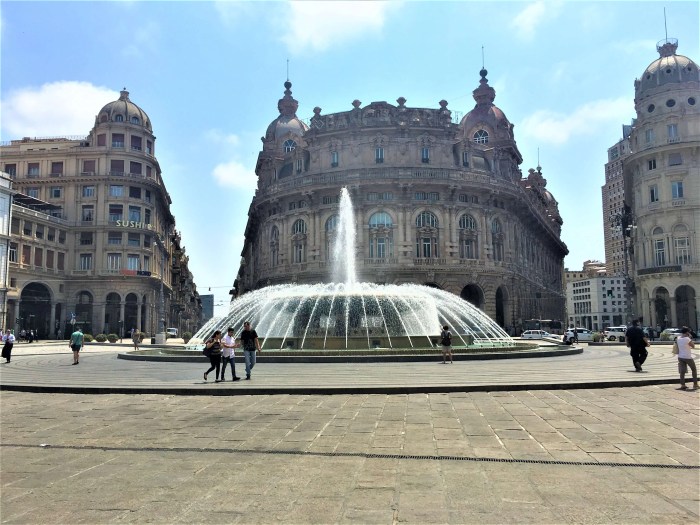

Genoa, a city steeped in maritime history, boasts a captivating blend of architectural styles and cultural treasures. From its awe-inspiring palaces to its vibrant historical districts, Genoa offers a journey through time. Exploring these landmarks provides a unique insight into the city’s past and present.
Iconic Landmarks
Genoa’s iconic landmarks stand as testaments to its rich history and architectural heritage. These structures, often showcasing intricate details and unique characteristics, are crucial to understanding the city’s development. Each landmark embodies a specific period and style, revealing aspects of Genoa’s past.The five most iconic landmarks include the Palazzo Ducale, the Porto Antico, the Cathedral of San Lorenzo, the Aquarium of Genoa, and the Via Garibaldi.
- Palazzo Ducale: This magnificent palace, built in the 14th century, exemplifies the city’s powerful past as a major trading hub. Its Gothic and Renaissance architecture is striking, featuring intricate details and imposing facades. The palace served as a symbol of Genoese power and prestige. Its courtyards and chambers offer glimpses into the lives of the dukes and powerful families.
- Porto Antico: This revitalized harbor district, once a bustling port, now hosts a variety of attractions. Its modern structures, alongside historical elements, reflect Genoa’s transition from a seafaring power to a vibrant urban center. The waterfront promenade and numerous restaurants showcase the district’s transformation into a popular tourist destination.
- Cathedral of San Lorenzo: This imposing cathedral, with its impressive façade, stands as a symbol of Genoa’s religious and cultural significance. Its architectural style blends Romanesque and Gothic influences, a reflection of the city’s historical evolution. The cathedral’s interior, with its rich history and artwork, provides a deeper insight into Genoa’s faith.
- Aquarium of Genoa: The Aquarium, a modern marvel, showcases the beauty and diversity of the marine world. Its vast collection of aquatic species from around the globe makes it a popular attraction. The aquarium also plays an important role in marine conservation efforts.
- Via Garibaldi: This historic street, with its elegant buildings and shops, exemplifies Genoa’s rich history. Its architecture, with a mix of styles, ranging from the 18th century to the 20th century, highlights Genoa’s continuous development. This street is a great place to soak in the atmosphere and explore the city’s shopping options.
Historical Districts
Genoa’s historical districts each have a distinct character and architectural style. Understanding these differences allows visitors to appreciate the evolution of the city’s architecture and urban planning.
- The Old Town (Centro Storico): The heart of Genoa, this district showcases a blend of narrow streets, historic buildings, and piazzas. The medieval architecture is prominent, with its narrow alleyways and traditional houses.
- The Upper Town (Supraporto): This elevated district, with its panoramic views, showcases the city’s development over time. The architecture here reflects a mix of styles, from ancient to modern. The views from the district’s vantage points are spectacular.
- The Harbor District (Porto Antico): As mentioned before, this district represents a modern transformation of a historic port. The mix of modern architecture and preserved historical elements creates a unique urban landscape.
Museums
Genoa boasts a collection of significant museums, each with unique historical and cultural importance.
| Museum | Collection | Significance | Opening Hours | Ticket Prices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galata Museo del Mare | Maritime history, including ship models, and nautical instruments. | Highlights Genoa’s prominent role in maritime trade. | Check website for schedule | Check website for pricing |
| Museo di Palazzo Bianco | Art collection spanning several centuries. | Presents a significant collection of paintings and sculptures from the 14th to the 18th century. | Check website for schedule | Check website for pricing |
| Museo d’Arte Orientale | Asian art, including ceramics, paintings, and sculptures. | Presents a rich collection of Asian art, showcasing diverse artistic styles and techniques. | Check website for schedule | Check website for pricing |
Top 10 Places to Visit
Genoa offers a diverse range of places to visit, each with a unique historical and cultural significance.
- Palazzo Ducale
- Porto Antico
- Cattedrale di San Lorenzo
- Museo di Palazzo Bianco
- Acquario di Genova
- Via Garibaldi
- Ripa di Ponente
- Castello di San Giorgio
- Museo di Arte Orientale
- Galata Museo del Mare
Exploring the City
Genoa, with its intricate network of streets and historical landmarks, is best explored at a relaxed pace. Understanding the city’s transportation options and choosing the right neighborhoods will significantly enhance your experience. Whether you prefer a leisurely stroll, a guided tour, or a comfortable stay in a charming neighborhood, Genoa offers something for everyone.
Transportation Options
Genoa provides various transportation options to navigate the city efficiently. Public transportation is a convenient and cost-effective way to reach major attractions. The Ligurian Region’s efficient train network connects Genoa to other cities in the region. The city’s extensive bus network provides access to more remote areas and neighborhoods. Taxis are readily available and can be a convenient option for longer distances or when you need a quicker transfer.
Walking is an excellent way to experience the city’s charm, particularly for shorter distances and exploring the pedestrian-friendly areas.
Walking Tours
Several walking tours cater to different interests and timeframes. These tours provide an enriching perspective on the city’s history, architecture, and culture. A typical walking tour will last approximately 2-3 hours and cover key sights, such as the historic center, Piazza De Ferrari, and the harbour. Guided walking tours can be booked directly with local tour operators or through online platforms.
These tours offer insights into the city’s past and present, providing a unique experience for visitors.
Neighborhoods to Stay
Genoa offers diverse neighborhoods, each with its unique atmosphere and charm. The historic center, with its narrow streets and ancient buildings, provides a captivating experience. The proximity to key attractions like the Aquarium and the harbor makes it an ideal choice for those wanting to explore the city’s highlights. For a more modern and vibrant experience, consider staying in the Porto Antico area.
This area offers a mix of historical and contemporary elements. Its location near the harbor and entertainment venues adds to its appeal. The residential neighborhoods around the city center offer a quieter atmosphere, with a mix of cafes and shops.
Planning a trip to Genoa, Italy? It’s a fantastic city with a rich history, delicious food, and stunning architecture. While exploring the charming streets and vibrant atmosphere, consider also visiting the captivating East Neuk coast of Scotland, a truly remarkable destination for a change of scenery. Visiting East Neuk coast Scotland offers a different kind of charm, but either way, you’ll be sure to create unforgettable memories, and Genoa is definitely worth a visit for its historical sites, vibrant port, and delicious Ligurian cuisine.
Accommodation Comparison
| Accommodation Type | Price Range (Approximate) | Amenities | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luxury Hotels | €200+ per night | High-end amenities, fine dining, spa | Historic center, Porto Antico |
| Boutique Hotels | €100-€200 per night | Unique character, comfortable rooms, often with breakfast | Historic center, near attractions |
| B&Bs | €50-€150 per night | Homestays, often with breakfast, charming atmosphere | Historic center, residential neighborhoods |
| Hostels | €20-€50 per night | Social atmosphere, budget-friendly, dorms and private rooms | City center, close to transport hubs |
This table provides a general comparison of accommodation options in Genoa, considering price, amenities, and location. Factors like the specific hotel or B&B, and the season can affect prices. Consider your budget and preferences when making your choice.
Culinary Delights
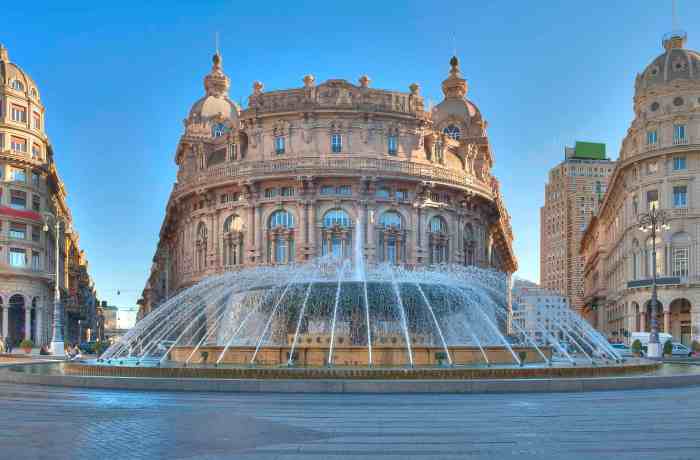

Genoa’s culinary scene is a vibrant reflection of its Ligurian heritage, showcasing a unique blend of fresh seafood, hearty vegetables, and aromatic herbs. The region’s proximity to the sea profoundly influences the cuisine, with seafood playing a central role in many traditional dishes. This rich culinary tapestry, woven with local ingredients, offers a truly unforgettable gastronomic experience.Ligurian cuisine, distinct from other Italian regions, is characterized by its emphasis on simplicity and the use of high-quality, locally sourced ingredients.
The freshness of the seafood, the vibrant colors of the vegetables, and the delicate flavors of the herbs create a harmonious symphony of tastes that are both familiar and unexpected.
Iconic Genoese Dishes
Genoese cuisine boasts a collection of iconic dishes that capture the essence of the region’s culinary identity. These dishes are not just meals; they are stories of tradition and passion, passed down through generations.
- Focaccia Genovese: This flatbread, a staple of Ligurian cuisine, is characterized by its simple yet satisfying flavor profile. Made with flour, water, and olive oil, it can be enhanced with various toppings, from simple rosemary and oregano to olives, anchovies, or vegetables. The dough is often brushed with olive oil, resulting in a crispy exterior and a soft interior.
- Trofie al Pesto: This dish epitomizes the region’s love for fresh ingredients. Trofie, a type of pasta with a unique, slightly irregular shape, is tossed with pesto, a vibrant green sauce made from basil, pine nuts, garlic, Parmesan cheese, and olive oil. The combination of the pasta’s texture with the pesto’s flavor creates a harmonious culinary experience.
- Farinata: A savory chickpea pancake, farinata is a simple yet delicious dish. Made with chickpea flour, water, and olive oil, it is often served hot, with a slightly crispy exterior and a fluffy interior. It’s a perfect accompaniment to a light meal or a tasty snack.
- Pesto alla Genovese: A cornerstone of Ligurian cuisine, pesto alla Genovese is more than just a sauce; it’s a testament to the region’s appreciation for fresh herbs. This classic pesto is prepared with basil, garlic, pine nuts, Parmesan cheese, and extra virgin olive oil. Its vibrant green color and rich flavor make it a must-try for any visitor.
- Sarde in Saor: This dish, which features sardines cooked in a tomato sauce, showcases the region’s commitment to fresh seafood. The sardines are typically cooked in a flavorful sauce, often incorporating onions, tomatoes, and herbs, highlighting the delicate flavor of the fish.
Comparison with Other Italian Cuisines
Ligurian cuisine differs from other Italian regional cuisines in its pronounced emphasis on fresh seafood and the use of local herbs and vegetables. While other regions might incorporate richer sauces or heavier meats, Ligurian cuisine often prioritizes the natural flavors of the ingredients. For instance, the use of pesto in Liguria is a defining feature, rarely found in other Italian regions in such a prominent role.
Recommended Restaurants
Genoa offers a diverse range of dining options, catering to various tastes and budgets.
- Seafood Restaurants (Mid-range to High-end): These restaurants typically offer fresh catches of the day, prepared with simple yet elegant techniques. Many restaurants are located near the harbor, providing an authentic ambiance.
- Traditional Trattorias (Budget-friendly): These restaurants often serve traditional Genoese dishes at affordable prices, offering an authentic taste of local cuisine.
- Modern Italian Restaurants (Mid-range to High-end): These establishments frequently blend traditional Ligurian techniques with modern culinary approaches, creating innovative dishes that still respect the region’s culinary heritage.
Traditional Genoese Desserts
Ligurian desserts often showcase the region’s commitment to fresh ingredients.
| Dessert | Ingredients | Cultural Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Biscotti | Flour, sugar, eggs, almonds | A classic Italian cookie, often enjoyed with coffee or tea. |
| Cantucci | Flour, sugar, eggs, almonds | A crunchy almond biscuit, perfect for dipping in Vin Santo. |
| Fave di San Giovanni | Peas, sugar, almonds | A traditional dessert, usually served during the summer. |
| Torta di Mele | Apples, sugar, flour, butter | A simple apple pie, with a traditional taste. |
| Pasticciotto | Dough, pastry cream, candied fruit | A sweet pastry with a rich filling. |
Cultural Experiences: Genoa Italy Travel Guide
Genoa’s rich history is woven into the very fabric of its cultural experiences. From the vibrant art scene to the lively festivals, the city offers a unique blend of tradition and modernity. Exploring these facets provides a deeper understanding of Genoese identity and its contributions to Italian culture.Genoa’s artistic heritage is multifaceted, reflecting the city’s maritime history, its bustling trade, and its enduring connection to the Mediterranean.
This cultural tapestry is further enriched by the city’s vibrant festivals and local markets, where unique crafts and products come to life.
Art Scene
Genoa boasts a significant art scene, with numerous galleries showcasing a diverse collection of works. Notable artists have contributed to the city’s artistic landscape, including local talents alongside internationally renowned figures. The city’s artistic heritage is reflected in its architecture, public art installations, and the works housed in various galleries.
Festivals and Events
Genoa hosts a calendar of festivals and events throughout the year, many with deep historical roots. These celebrations, such as the Palio di Ponte dei Mille, highlight the city’s history and cultural significance. The events are often steeped in tradition, offering a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of Genoa. These festivals and events serve as vital expressions of Genoese identity.
Local Markets and Shops
Genoa’s markets are vibrant hubs of activity, showcasing local products and crafts. From the colorful stalls of the Rialto market to artisan workshops, the city offers a unique opportunity to discover local crafts and unique products. These markets provide a sensory experience, connecting visitors with the city’s cultural heritage and its present. The shops in Genoa often showcase traditional crafts and local design elements.
Nightlife
Genoa’s nightlife scene offers a variety of options for entertainment, from cozy bars to lively clubs. The city’s bars often feature traditional Italian music, while clubs host DJs and live bands, reflecting the diverse tastes of the local community. These venues offer a range of entertainment choices, catering to diverse preferences and tastes.
Art Galleries
| Gallery Name | Collection Highlights | Opening Hours |
|---|---|---|
| Palazzo Bianco | Italian paintings from the 14th to 18th centuries, including works by masters like Tiepolo and Canaletto. | Tuesday-Sunday, 9am-7pm |
| Palazzo Rosso | Important works by Italian masters such as Rubens and Rembrandt, alongside a strong collection of Genoese paintings. | Tuesday-Sunday, 9am-7pm |
| Museo d’Arte Orientale | Extensive collection of East Asian art, including ceramics, sculptures, and paintings. | Wednesday-Sunday, 10am-6pm |
| Galleria di Palazzo Ducale | Permanent exhibitions of Italian art, including works by local artists and significant historical pieces. | Tuesday-Sunday, 10am-6pm |
Note: Opening hours may vary; it is recommended to check the official website for the most up-to-date information.
Practical Information
Genoa, a vibrant city brimming with history and culture, is ready to welcome you! Navigating the city’s intricacies becomes seamless once you understand the practicalities. This section will cover visa requirements, currency, local customs, safety tips, and essential phrases for your smooth journey.
Visa Requirements, Genoa italy travel guide
Genoa, as part of Italy, generally falls under the Schengen Area visa requirements. Citizens of many countries can enter Italy for short-term stays without a visa. However, it’s crucial to check the specific visa regulations for your nationality on the official Italian embassy or consulate website. This will ensure a hassle-free arrival. Pre-checking visa requirements saves you from potential issues at the border.
Currency Exchange and Payment Options
The official currency of Italy is the Euro (€). You’ll find numerous currency exchange bureaus throughout the city, often conveniently located near major tourist attractions and train stations. Furthermore, ATMs are readily available, providing a convenient way to withdraw cash. Credit cards are widely accepted in most shops and restaurants, making transactions easy and efficient.
Local Customs and Etiquette
Italian culture places a high value on politeness and respect. Be mindful of the local customs and traditions. It’s customary to greet people with a handshake or a kiss on the cheek (depending on the region). When visiting religious sites, dress modestly. Remember to be respectful of local customs and traditions to ensure a positive experience for everyone.
These thoughtful actions create a welcoming environment for visitors.
Staying Safe and Secure in Genoa
Like any major city, taking precautions to stay safe is essential. Be vigilant about your belongings, especially in crowded areas. Keep your valuables secure, and avoid displaying large sums of cash. Trust your instincts, and if you feel uneasy, seek help from a trusted member of staff or security personnel. These precautions ensure a safe and enjoyable stay.
Useful Phrases in Italian
| Italian Phrase | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Buongiorno | Good morning |
| Buonasera | Good evening |
| Grazie | Thank you |
| Prego | You’re welcome |
| Scusi | Excuse me |
| Mi scusi | Excuse me (more formal) |
| Per favore | Please |
| Arrivederci | Goodbye |
| Quanto costa? | How much does it cost? |
| Parla inglese? | Do you speak English? |
Learning these basic phrases will enhance your interactions with locals and create a more positive experience. Use them thoughtfully, and you’ll find yourself connecting with the city and its people on a deeper level.
Day Trips and Excursions
Venturing beyond the city walls of Genoa offers a wealth of opportunities to explore the Ligurian Riviera’s charm. From picturesque coastal towns to hilltop villages steeped in history, day trips from Genoa provide a glimpse into the region’s diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage. These excursions offer a fantastic way to experience the beauty of Liguria beyond the city’s bustling streets.Exploring nearby towns and attractions by day trip allows for a deeper appreciation of the region’s varied character, moving beyond the urban landscape to experience authentic Italian life and scenery.
Day Trip Destinations from Genoa
Genoa’s strategic location allows for easy access to a variety of charming destinations. Here are some highlights, categorized by interest, to inspire your day trips.
| Destination | Duration (approx.) | Transportation | Historical/Cultural Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portofino | Full Day | Train to Santa Margherita Ligure, then ferry or taxi to Portofino. | Famous for its picturesque harbor, colorful houses clinging to the hills, and luxurious atmosphere. A popular destination for tourists, it offers stunning views and a unique blend of natural beauty and historical charm. |
| Rapallo | Half Day | Train or bus. | A charming coastal town with a beautiful promenade, historic buildings, and excellent seafood restaurants. It offers a relaxed atmosphere perfect for a leisurely exploration. |
| Camogli | Full Day | Train to Santa Margherita Ligure, then ferry. | Known for its beautiful beaches, colorful houses, and picturesque harbor. The town’s historical significance lies in its maritime heritage and its role as a fishing port. |
| Sestri Levante | Full Day | Train. | A coastal town with two distinct harbors, one facing the sea and the other facing the bay. It is a popular destination for its beaches, picturesque views, and historical buildings. |
| Montemarcello | Full Day | Train to Moneglia or Levanto, then bus or taxi. | A charming hilltop village with breathtaking views of the Ligurian coastline. Its historical significance stems from its location, commanding a strategic vantage point over the region. |
Comparing Day Trip Options
The best day trip for you depends on your interests. If you appreciate picturesque harbors and colorful houses, Portofino or Camogli are excellent choices. For a more relaxed atmosphere and a taste of Ligurian seafood, Rapallo or Sestri Levante might be better suited. Those interested in panoramic views and a touch of history will find Montemarcello appealing.
Consider the time you have available and the mode of transportation when making your decision.
Transportation Options
The most common and convenient way to reach these destinations from Genoa is by train. The Ligurian train network connects Genoa to numerous towns along the coast, offering a relatively fast and efficient way to travel. Buses are also available, offering a more affordable option, but may take slightly longer. Ferries are another viable option, particularly for destinations like Portofino, and Camogli, where they provide scenic access.
Consider these factors when choosing the best transportation method for your day trip.
Epilogue
This Genoa Italy travel guide has provided a comprehensive overview, highlighting the city’s historical significance, architectural marvels, culinary delights, and cultural experiences. From the bustling streets to the hidden courtyards, Genoa offers a unique Italian adventure. Plan your trip and prepare to be captivated by this beautiful coastal city!