Forest tower spiral walkway Denmark Zealand offers a captivating experience, winding through the heart of nature. Imagine a mesmerizing journey up a spiraling path, nestled within a dense forest, with stunning views from the tower. This architectural marvel, a unique blend of natural beauty and engineering prowess, draws inspiration from the landscapes of Denmark and New Zealand, each with its own distinct character.
This exploration delves into the architectural design, historical context, environmental impact, visitor experience, and the profound local community engagement these structures foster. From the initial design concept to the finished product, each step in the creation process is carefully considered. The blend of natural beauty and human ingenuity makes for a unique and memorable experience.
Introduction to Forest Tower Spiral Walkway
A forest tower spiral walkway is a unique architectural structure that seamlessly blends nature and human design. These walkways, often constructed within or around forested areas, provide visitors with a captivating perspective of the surrounding environment while offering a unique and engaging experience. They typically feature a spiral staircase or ramp that ascends the tower, allowing visitors to progressively ascend through the trees and foliage.These structures employ innovative architectural and engineering principles to create a stable and safe platform for visitors.
Design considerations include factors such as load-bearing capacity, material selection, and environmental impact. Careful attention to detail is essential in achieving both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. The design of these structures is intended to complement the surrounding environment, not dominate it.
Architectural and Design Principles
Forest tower spiral walkways are meticulously designed to incorporate the principles of sustainable architecture. Their design emphasizes harmony with the natural landscape, often using locally sourced materials and employing construction methods that minimize environmental impact. The overall design prioritizes visitor safety and enjoyment. This includes the consideration of factors such as the slope of the spiral ramp or staircase, handrails, and the overall structural integrity of the tower.
Materials Used in Construction
The choice of materials for forest tower spiral walkways is often influenced by factors like local availability, durability, and aesthetics. Common materials include timber, steel, concrete, and glass. Timber is frequently used for its strength and aesthetic appeal, while steel provides structural support. Concrete offers durability and a stable base, and glass offers stunning views of the surrounding forest.
The use of sustainable materials is a significant consideration, often guiding material selection.
Examples in Denmark and New Zealand
Denmark and New Zealand have each developed unique forest tower spiral walkways, showcasing a range of design and construction techniques. These structures offer visitors a breathtaking experience of the surrounding forest ecosystems.
Comparison of Structural Features
| Feature | Example A (Denmark) | Example B (New Zealand) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Predominantly sustainably sourced timber, with steel for structural support. | Combination of locally sourced timber for the spiral ramp and glass panels for viewing platforms. |
| Height | Approximately 25 meters, offering panoramic views of the surrounding forests. | Approximately 30 meters, featuring multiple viewing platforms at different heights. |
| Spiral Ramp/Staircase | A gentle spiral ramp, suitable for various ages and abilities. | A slightly steeper spiral ramp, designed for a more adventurous experience. |
| Structural Support | A central support structure, with the timber forming the spiral walkway. | A combination of internal and external supports, with a focus on the aesthetic integration of the structural elements. |
| Environmental Considerations | Minimal impact on the forest ecosystem, with careful consideration of the surrounding flora and fauna. | Use of sustainable materials and construction methods to minimize the environmental footprint. |
Historical Context and Inspiration
The Forest Tower Spiral Walkway project, a testament to innovative design and environmental consciousness, draws inspiration from a rich tapestry of historical precedents and contemporary influences. Understanding these influences helps illuminate the unique characteristics and purpose of these structures. Their design, beyond mere aesthetics, reflects a deeper understanding of human interaction with nature and a commitment to sustainable development.The concept of elevated walkways within natural settings has evolved over centuries.
Early examples, though less technologically sophisticated, demonstrate a human desire to connect with the forest canopy and observe the surrounding ecosystem. This fascination with aerial perspectives has been a driving force behind many structures throughout history.
Evolution of Similar Structures
Early forms of elevated walkways can be traced back to indigenous communities who utilized natural features or rudimentary platforms for observation and navigation. The development of more complex structures, such as suspension bridges and viewing towers, showcased growing technological capabilities. These earlier structures laid the groundwork for the modern design principles employed in the Forest Tower Spiral Walkways. Examples include the iconic Eiffel Tower, which, while not a walkway, exemplifies the fascination with elevated perspectives and engineering feats.
That incredible forest tower spiral walkway in Denmark and Zealand is truly breathtaking. Imagine the views from the top, spiraling down through the trees. It’s inspiring to see how architecture can blend with nature so seamlessly. Speaking of inspiring places, the Academy Museum of Motion Pictures is a must-see, with its impressive collection and exhibitions. academy museum motion pictures offers a unique experience, and perhaps, similar to the serene atmosphere of the forest tower.
The tower’s design and construction highlight innovative ideas in sustainable architecture, making it a must-see for anyone interested in the future of outdoor spaces.
Influences and Inspirations Behind the Design
The designs of these spiral walkways are undeniably influenced by both the natural environment and the principles of modern architecture. The spiral form, often seen in nature, offers a dynamic and visually engaging experience, allowing visitors to traverse the forest canopy in a continuous and captivating manner. The design also incorporates elements of sustainable construction, using locally sourced materials and minimizing environmental impact.
The overall design philosophy prioritizes integration with the natural surroundings.
Cultural and Environmental Considerations, Forest tower spiral walkway denmark zealand
The construction of these walkways necessitates a deep understanding of the local ecology and cultural values. Careful consideration is given to the impact on local flora and fauna. The pathways are designed to minimize disturbance and maintain the natural character of the forest. Community engagement and input are crucial to ensure the project aligns with local traditions and values.
For instance, incorporating indigenous knowledge and practices into the design process is essential for sustainable development.
Societal and Economic Impacts on Local Communities
The Forest Tower Spiral Walkways can significantly impact local communities through economic development. Increased tourism and related activities can create jobs and stimulate the local economy. These projects often serve as educational hubs, fostering appreciation for the environment and promoting environmental awareness. The economic benefits must be balanced with the need to preserve the natural environment and avoid exploitation.
Careful planning and community involvement are key to ensuring these projects benefit all stakeholders.
Timeline of Development
| Year | Denmark | New Zealand |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Conceptual design phase initiated. | Preliminary research and community consultation begin. |
| 2021 | Detailed design and permit application process. | Environmental impact assessments completed. |
| 2022 | Construction commences. | Construction tenders issued and awarded. |
| 2023 | Walkway construction finalized. | Walkway open to public. |
| 2024 | Tourism and economic benefits assessed. | Long-term sustainability plans developed. |
Environmental Impact and Sustainability: Forest Tower Spiral Walkway Denmark Zealand
The construction of spiral walkways, particularly in forested areas, presents a complex interplay of environmental benefits and challenges. Careful consideration of material choices, construction techniques, and the potential impact on local ecosystems is crucial for minimizing negative consequences and maximizing positive contributions to the environment. Sustainable practices are paramount in ensuring these structures stand as testaments to environmental responsibility rather than burdens on the surrounding landscape.The very nature of these structures requires a nuanced understanding of the local ecosystem.
Design decisions, from the selection of materials to the footprint of the walkway, directly influence the impact on biodiversity, soil health, and water cycles. Careful planning and execution can transform these structures into tools for ecological conservation, promoting awareness and fostering a deeper connection with the natural world.
Material Selection and Construction Methods
Sustainable construction demands a commitment to environmentally responsible materials and practices. The choice of materials directly impacts the carbon footprint of the project. Using locally sourced, reclaimed, or recycled materials reduces transportation emissions and minimizes the need for raw material extraction, thereby mitigating deforestation and habitat loss. Employing prefabricated components can also reduce on-site waste and construction time, further minimizing the environmental footprint.
Advanced construction techniques, such as minimizing concrete use and employing light-weight materials, contribute to reduced energy consumption throughout the project lifecycle. Construction methods should prioritize minimizing soil disturbance and preserving existing vegetation to maintain the natural integrity of the surrounding ecosystem.
Impact on Local Ecosystem
The construction of these walkways can have both positive and negative effects on the local ecosystem. Careful planning can minimize habitat fragmentation and disruption to wildlife movement. The structures themselves can serve as new habitats for certain species, offering diverse microclimates and refuge from predators. Monitoring wildlife interactions with the walkways and adapting design elements based on observations is critical for ensuring the structure supports, rather than hinders, biodiversity.
The careful selection of materials, including native plants for landscaping around the walkway, promotes ecological resilience and enhances the aesthetic integration of the structure with the natural environment.
Environmental Benefits and Challenges in Different Locations
| Location | Environmental Benefits | Environmental Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Dense Forest (e.g., temperate rainforests) | Potential for increased awareness and conservation efforts; opportunities for habitat creation through strategically placed planting; reduced impact on existing habitats due to minimal land disturbance. | Potential for increased human disturbance; potential for disruption of existing wildlife corridors; increased risk of erosion or sedimentation if not properly designed. |
| Mountainous Regions (e.g., alpine meadows) | Opportunities for promoting responsible tourism; potential for generating revenue for local communities; minimal impact on fragile alpine ecosystems if construction techniques are appropriate. | Potential for destabilizing slopes; disruption of delicate alpine ecosystems; increased risk of landslides if construction is not designed for the unique geological conditions. |
| Coastal Regions (e.g., mangrove forests) | Opportunities for education and advocacy on coastal preservation; potential for supporting local fisheries if designed in conjunction with local ecological expertise. | Increased risk of habitat loss if construction disrupts natural processes such as water flow; potential for damage to existing ecosystems due to construction activities. |
Visitor Experience and Accessibility
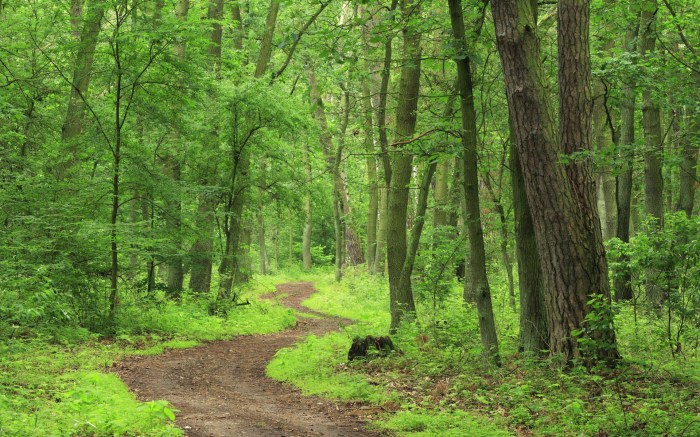

Stepping onto the Forest Tower Spiral Walkway is more than just a visit; it’s an immersive experience. The unique design, blending seamlessly with the surrounding forest, creates a feeling of connection with nature. Visitors are drawn into a world of towering trees and winding pathways, experiencing the forest from a completely new perspective. The spiral ascent provides a gradual and engaging journey, offering stunning views at each turn.The design prioritizes safety and accessibility, ensuring visitors of all abilities can enjoy the experience.
From the sturdy handrails to the carefully graded paths, the walkway is crafted with meticulous attention to detail. This allows for a truly inclusive experience, opening the forest to a wider audience and promoting environmental appreciation.
Safety Measures
The safety of visitors is paramount. Robust handrails are strategically positioned along the entire length of the walkway, providing stability and security, especially during moments of high wind or uneven terrain. These handrails are not only functional but also aesthetically integrated with the surrounding environment, complementing the natural beauty of the forest. The entire walkway is meticulously maintained, with regular inspections and repairs to ensure the integrity of the structure.
That stunning spiral walkway in the Danish forest tower is truly breathtaking. It’s inspiring to see such innovative design, but it got me thinking about the environmental impact of construction materials. Considering Marriott International’s recent commitment to eliminating plastic waste, marriott international plastics ban , perhaps sustainable materials could be used in future projects like this, aligning with responsible tourism practices.
Hopefully, the forest tower walkway will continue to be a beautiful and environmentally conscious example for years to come.
Emergency exits and trained personnel are readily available in case of an incident.
Accessibility Features
The Forest Tower Spiral Walkway has been designed with accessibility in mind. This includes ramps for wheelchair users and adapted walkways for those with mobility limitations. Elevators are incorporated to ease access to different levels of the tower. Tactile paving is integrated into the path to provide directional guidance and orientation for visually impaired visitors. Furthermore, clear signage with Braille and large print is available at key points.
Sensory Experiences
The forest tower offers a multi-sensory experience. The gentle breeze rustling through the leaves, the sounds of birdsong, the scent of pine needles and damp earth – all combine to create a unique and memorable atmosphere. The gentle incline of the spiral pathway allows for a calm and meditative pace, encouraging reflection and mindfulness.
Visitor Feedback and Reviews
Visitor reviews consistently praise the breathtaking views and the immersive experience. Many comment on the peaceful atmosphere and the opportunity to connect with nature. Some visitors have highlighted the accessibility features as a significant plus, allowing them to fully enjoy the experience. “I was so impressed with the accessibility features. My friend, who uses a wheelchair, was able to enjoy every moment of the walk,” said one reviewer.
Accessibility Features Table
| Visitor Ability | Accessibility Feature |
|---|---|
| Wheelchair users | Ramps, elevators, adapted walkways |
| Mobility limitations | Ramps, adapted walkways, elevators, accessible restrooms |
| Visually impaired | Tactile paving, Braille signage, large print signage |
| Hearing impaired | Audio guides (optional), visual cues |
Architectural Design and Engineering
The Forest Tower Spiral Walkway, a testament to modern architectural ingenuity, demands a meticulous approach to structural design and engineering. Careful consideration of load-bearing capacity, material selection, and the interplay of form and function are critical to ensuring the walkway’s safety and aesthetic appeal. This section delves into the intricate details of the walkway’s design, examining the challenges encountered and the innovative solutions employed.The engineering of these structures involves a sophisticated understanding of forces, materials, and their interaction under dynamic conditions.
Factors like wind resistance, seismic stability, and pedestrian traffic patterns need to be carefully considered to ensure the long-term integrity and safety of the walkway. The design must also reflect the natural environment, harmonizing with the surrounding ecosystem while still maintaining structural integrity.
Ever heard of the stunning forest tower spiral walkway in Denmark/Zealand? It’s a truly unique architectural marvel, but did you know that Copenhagen also boasts incredible sculptures, like the giant trolls by Thomas Dambo? These whimsical creations, inspired by the fantastical world of copenhagen giants trolls sculptures thomas dambo , add another layer of wonder to the already captivating city.
The forest tower’s spiral design and its connection to nature, make it a perfect complement to the creative spirit found throughout Copenhagen.
Structural Design Analysis
The structural design of the walkways necessitates a comprehensive analysis of the anticipated loads. This involves modelling the walkway’s geometry, considering the distribution of pedestrian weight, and simulating potential environmental stresses. The design must ensure a safe and comfortable experience for all users, accommodating a range of potential conditions. Sophisticated computer modelling plays a critical role in verifying the structural integrity and optimizing the design.
The design also must be tailored to the specific terrain and environmental conditions.
Engineering Challenges
Constructing these structures presents a variety of engineering challenges. These include ensuring the walkway’s stability in dynamic conditions, such as high winds and varying temperatures. Ensuring the structural integrity against seismic activity is crucial in regions prone to earthquakes. The intricate spiral design itself presents challenges in maintaining the desired stability and safety throughout the entire structure.
The unique curvature of the walkways demands sophisticated calculations to manage stress points and ensure uniform load distribution. Furthermore, the integration of the walkway with the surrounding natural environment presents unique challenges that must be addressed to minimize environmental impact.
Advanced Materials and Technologies
The use of advanced materials and technologies is crucial in the construction of these structures. Lightweight yet strong materials, such as high-strength steel or advanced composites, can enhance the structural integrity without adding excessive weight. Pre-stressed concrete elements or innovative cable-supported systems can further contribute to the structural efficiency and aesthetics. Advanced materials often contribute to a lighter footprint, minimizing the impact on the environment.
Innovative construction techniques, such as 3D printing or modular construction, could offer further efficiencies in the future.
Design Approaches in Denmark and New Zealand
While both Denmark and New Zealand likely employ similar fundamental engineering principles, the specific design approaches may vary. Local building codes, environmental considerations, and cultural preferences might influence the choice of materials and construction methods. The design process might incorporate local materials to minimize the environmental impact. Further research would be needed to identify the unique design approaches used in each country.
Table of Structural Elements and Applications
| Structural Element | Specific Application |
|---|---|
| High-strength Steel Cables | Support for spiral sections, minimizing weight and maximizing structural strength. |
| Pre-stressed Concrete Slabs | Provide a strong foundation and support the walkway’s load, while managing stress points. |
| Composite Materials | Enhance the structure’s strength-to-weight ratio, and potentially reduce construction costs. |
| Advanced Anchoring Systems | Secure the walkway to the surrounding natural terrain, ensuring stability in all conditions. |
Local Community Engagement and Tourism
The Forest Tower Spiral Walkway, a testament to innovative design and environmental consciousness, holds significant potential for enriching the lives of local communities. Beyond its architectural beauty, it can serve as a catalyst for economic growth, cultural preservation, and community bonding. The success of such a project hinges on proactive engagement with local stakeholders, ensuring that the benefits are widely shared.
Role of Local Communities in Development
Local communities play a crucial role in the development and operation of such structures. Their input during the design phase can ensure that the walkway aligns with local needs and preferences. This can involve incorporating local materials in construction, respecting traditional architectural styles, and ensuring the walkway is accessible to individuals with diverse needs. Involving local artisans in the design and construction process can also foster local employment and preserve traditional skills.
Economic Impact on Local Businesses
The walkway can stimulate economic activity by attracting tourists and creating opportunities for local businesses. Restaurants, shops, and accommodation providers in the vicinity can see an increase in revenue as visitors spend money on goods and services. Local guides and tour operators can also benefit by offering experiences centered around the walkway, which can provide employment and generate income.
For example, the development of the Eiffel Tower in Paris significantly boosted the local economy, attracting millions of tourists and providing numerous business opportunities.
Promoting Local Culture and Heritage
The Forest Tower Spiral Walkway can serve as a platform for showcasing local culture and heritage. Local crafts, traditions, and stories can be integrated into the visitor experience. For instance, themed events and exhibitions could highlight the region’s unique history and traditions. This can help foster a sense of pride and belonging among local communities, while simultaneously offering a unique cultural experience for visitors.
Attracting Tourists
The walkway’s unique design and location can attract tourists from across the country and internationally. Its accessibility and ease of use can make it a popular destination for families, nature enthusiasts, and photography lovers. Marketing campaigns targeted at specific demographics can further increase visitor numbers. By highlighting the unique experiences the walkway offers, such as breathtaking views and opportunities for exploration, the local tourism industry can be boosted.
Economic Benefits and Challenges for Local Communities
| Economic Benefits | Economic Challenges |
|---|---|
| Increased tourism revenue for local businesses (restaurants, shops, accommodations). | Competition with other attractions in the region for tourists’ attention. |
| Creation of new jobs in construction, maintenance, and tourism sectors. | Potential for increased traffic congestion and strain on local infrastructure. |
| Enhanced reputation and visibility of the region. | Potential for price inflation in local goods and services. |
| Opportunities for local artisans and cultural preservation. | Balancing the needs of tourists with the protection of the natural environment. |
| Increased property values in the surrounding areas. | Need for effective waste management and environmental protection strategies. |
Future Trends and Innovations

Forest tower spiral walkways, like those envisioned for Denmark and New Zealand, represent a fascinating intersection of architecture, nature, and visitor experience. As the concept gains traction, the future holds exciting possibilities for advancements in design, construction, and the overall visitor journey. This exploration delves into potential developments, emerging technologies, and innovative approaches to elevate these unique structures.The increasing demand for sustainable and immersive experiences is driving innovation in this field.
This trend extends beyond mere aesthetics, encompassing the integration of technology, art, and environmental consciousness. Designers and engineers are constantly seeking new ways to optimize the visitor experience, while maintaining respect for the surrounding environment.
Potential Developments in Design and Construction
The design and construction of future forest tower spiral walkways will likely incorporate more advanced materials and construction techniques. Lightweight, yet durable composites might become increasingly prevalent, allowing for taller and more complex structures. 3D printing could revolutionize the construction process, enabling customized designs and potentially reducing construction time and costs. Pre-fabricated modules could also play a role in faster and more efficient assembly.
Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are poised to transform the visitor experience within these structures. Interactive displays and augmented reality (AR) applications can provide enriching insights into the local flora and fauna, the history of the forest, or the architectural process itself. Sensors and data analytics can monitor visitor flow, environmental conditions, and structural integrity, allowing for real-time adjustments and proactive maintenance.
This data-driven approach could significantly improve visitor comfort and safety.
Innovative Approaches to Enhance Visitor Experience
Future forest tower spiral walkways could integrate dynamic lighting systems, creating immersive visual experiences that change throughout the day. The integration of sound design and music can enhance the visitor’s connection with the natural environment. Interactive art installations along the walkway could offer unique and engaging experiences, enhancing visitor interaction and interpretation. Sustainable transportation systems, like electric vehicles or cable cars, can contribute to a more eco-conscious experience for visitors.
Incorporating Art and Culture
Integrating art and culture into the design of these walkways is crucial. Local artists could be commissioned to create unique sculptures or installations that reflect the region’s cultural heritage. The incorporation of local stories and legends through interactive exhibits or interpretive panels can deepen the visitor’s understanding and appreciation for the area. The walkways themselves could become living art pieces, seamlessly integrating with the surrounding natural landscape.
Emerging Trends in Forest Tower Spiral Walkway Design
| Trend | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Materials | Prioritizing the use of recycled, renewable, and locally sourced materials. | Bamboo, timber from sustainable forests, recycled plastics. |
| Smart Technology Integration | Implementing sensors, interactive displays, and data analytics to enhance visitor experience and maintenance. | AR apps, real-time environmental data displays, automated lighting systems. |
| Dynamic Visual Experiences | Using dynamic lighting, projections, and interactive displays to enhance the visitor experience and connection with the natural environment. | Changing light shows synchronized with the time of day, projected stories onto the structure. |
| Immersive Audio Experiences | Utilizing sound design and music to create a more engaging and memorable experience. | Sound installations mimicking forest sounds, guided audio tours. |
| Community Engagement | Involving local communities in the design process and implementation of the structure. | Workshops, exhibitions, and cultural performances. |
Final Summary
In conclusion, forest tower spiral walkways in Denmark and New Zealand represent a harmonious blend of nature and human innovation. These structures, carefully crafted and designed, offer a unique visitor experience while also integrating seamlessly with the local environment. Their enduring appeal lies in their ability to inspire awe, foster appreciation for nature, and stimulate economic growth within the local communities they serve.