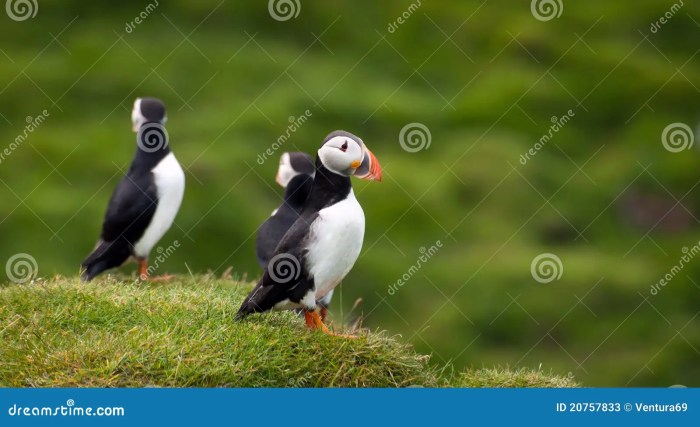
Puffling Patrol Westman Islands: a dedicated group safeguarding the future of these adorable birds. Nestled in the dramatic beauty of the Westman Islands, this patrol plays a vital role in the local ecosystem, meticulously monitoring and protecting the precious puffling population. Their efforts, spanning decades, have fostered a deep connection between conservation and the islands’ rich avian life.
From the initial introduction of the patrol to the varied species of birds it protects, the Westman Islands’ puffling patrol is a testament to human dedication in the face of conservation challenges. This patrol isn’t just about saving birds; it’s about nurturing the entire ecosystem and ensuring the future of these remarkable islands.
Introduction to Puffling Patrol (Westman Islands)

The Westman Islands Puffling Patrol is a dedicated volunteer initiative focused on safeguarding the delicate lives of puffin chicks, specifically within the unique ecosystem of the Westman Islands. Their work encompasses a broad range of activities, from monitoring chick development to addressing potential threats, all with the goal of ensuring the survival of these iconic seabirds.This crucial effort is vital for maintaining the ecological balance of the Westman Islands, as puffins play a significant role in the local food web and contribute to the overall biodiversity of the region.
The patrol’s meticulous observations and timely interventions directly impact the future of these fascinating creatures.
I’ve been captivated by the Puffling Patrol in the Westman Islands lately. Seeing these adorable little puffins is truly heartwarming, a reminder of nature’s beauty. It made me think about how travel can be incredibly healing, especially for women of color facing breast cancer, like in the healing through travel for black women breast cancer initiative.
Hopefully, the Puffling Patrol will inspire a similar sense of peace and strength in those battling this tough disease. The islands are just so inspiring.
Geographical Location and Relevance
The Westman Islands, situated off the southern coast of Iceland, boast a unique combination of rugged landscapes and rich marine life. This geographical isolation and abundance of marine resources make the islands a vital breeding ground for various seabirds, including puffins. The islands’ proximity to the open ocean and surrounding currents provide the necessary food sources for the puffins, while the cliffs and sea caves offer safe nesting sites.
This specific location is crucial for the Puffling Patrol, as it dictates the specific challenges and opportunities for protecting the puffin population.
Historical Context
The Puffling Patrol’s existence in the Westman Islands dates back to the early 2000s. Driven by a growing awareness of the threats facing puffin populations, local communities and conservationists collaborated to establish this dedicated patrol. Their initial focus was on understanding the puffin life cycle and identifying potential threats, such as human interference and predation. Over time, the patrol has evolved, adapting its strategies to address new challenges and expand its reach.
Significance in the Local Ecosystem
Puffins are integral to the Westman Islands’ ecosystem. Their presence influences the abundance of fish and other marine organisms, while their chicks are a significant source of food for some predators. The Puffling Patrol’s actions directly contribute to maintaining this intricate web of life. By protecting the puffin chicks, the patrol indirectly safeguards the entire ecosystem. Their activities help ensure the ongoing health and vitality of the Westman Islands’ natural environment.
Bird Species Associated with the Puffling Patrol
The Westman Islands are home to a variety of avian species, each with its own unique nesting habits. The Puffling Patrol’s focus is primarily on the puffin species, but they also monitor and document other birds nesting in the area.
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Nesting Habits |
|---|---|---|
| Fratercula arctica | Atlantic Puffin | Breed in colonies on cliffs and ledges, laying one to three eggs. |
| Larus spp. | Gulls | Nesting sites vary, often on ground or in bushes near the colony |
| Fulmarus glacialis | Fulmar | Nest in crevices and burrows on cliffs. |
| Uria aalge | Guillemot | Breed in colonies on cliffs and ledges, laying one egg. |
Puffling Patrol Activities: Puffling Patrol Westman Islands
The Puffling Patrol in the Westman Islands plays a crucial role in safeguarding the delicate lives of puffin chicks, from hatching to fledging. Their tireless efforts contribute significantly to the overall health and population stability of the puffin colony. Dedicated volunteers and researchers work in tandem to ensure the well-being of these vulnerable young birds.The patrol’s activities extend beyond simple observation; they actively intervene when necessary to protect the pufflings from threats.
Their strategies are carefully designed to minimize disturbance to the natural environment while maximizing the chances of survival for the next generation of puffins.
Monitoring Puffling Development
The Puffling Patrol meticulously tracks the growth and development of the pufflings. This involves regular checks on the chicks’ health, including monitoring their weight, plumage development, and general activity levels. Detailed records are kept to assess trends and identify any potential issues early on. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention if a puffin chick displays signs of distress or illness.
Precise measurements, combined with observations of behaviour, are crucial in determining the health of the chicks and predicting potential problems. For example, consistent weight gain and the emergence of flight feathers indicate a healthy development trajectory.
Protecting Pufflings from Predators
Protecting pufflings from predators is a key aspect of the Puffling Patrol’s work. They employ a range of strategies, from deterring potential predators like gulls and foxes to physically removing any immediate threats. Deterrents might include strategically placed scarecrows or the use of noisemakers. In cases of direct predation, the patrol intervenes to remove the predator or relocate the threatened pufflings.
The patrol also educates the public about the importance of keeping a safe distance from the nesting sites, and the risks of feeding the pufflings. Careful consideration is given to each specific threat. For instance, the patrol might set up barriers to prevent foxes from accessing the burrows, or use deterrents to keep away aggressive gulls.
Challenges Faced in Different Seasons
The Puffling Patrol faces unique challenges across different seasons. Spring brings the delicate task of monitoring the hatching process, and ensuring the newly hatched pufflings receive proper care and support. Summer brings the responsibility of monitoring the pufflings’ growth and development, while fall sees a shift in focus to preparing for the pufflings’ departure. Winter, conversely, requires the patrol to focus on protecting the pufflings from potential hazards like severe weather and the potential for predation.
These challenges often require adapting strategies and resources.
Summary of Puffling Patrol Operations
| Activity | Goal | Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring Puffling Development | Identify and address potential issues early | Regular checks, detailed records, weight measurements, plumage observation |
| Protecting Pufflings from Predators | Minimize threats to puffling survival | Deterrents, intervention, public education, habitat protection |
| Responding to Seasonal Challenges | Ensure puffin survival through various seasons | Adaptive strategies, resource allocation, proactive measures for each season |
Impact of the Puffling Patrol
The Puffling Patrol in the Westman Islands has yielded remarkable results, demonstrating a positive impact on the local puffin population and the overall ecosystem. Its activities extend far beyond immediate puffin protection, contributing significantly to conservation awareness and fostering a stronger connection between the community and the natural world. This dedicated initiative has also had a positive ripple effect on tourism and the local economy.The Puffling Patrol’s core function is safeguarding puffin populations.
By monitoring nesting sites, intervening in cases of disturbance, and educating the public, the patrol has helped to reduce human-induced threats and create a more secure environment for the breeding success of these remarkable seabirds. This has, in turn, contributed to the long-term health and resilience of the Westman Islands’ ecosystem.
Positive Effects on Bird Population
The Puffling Patrol’s consistent monitoring and intervention have led to a noticeable increase in puffin fledgling survival rates. Reduced disturbance from human activity and effective predator control measures have contributed to a more stable and thriving breeding environment. By actively protecting nests and young puffins, the patrol directly impacts the population’s reproductive success, ultimately ensuring a healthy and growing population over time.
Long-Term Implications for the Ecosystem
The Puffling Patrol’s influence extends beyond the puffin population. The reduction in disturbance at puffin nesting sites has a cascading effect on other species within the ecosystem. A more secure breeding environment for puffins translates into a healthier and more diverse ecosystem, fostering a balance among all the interacting species. This contributes to the overall biodiversity of the Westman Islands, enhancing its ecological value.
Role in Raising Awareness
The Puffling Patrol plays a critical role in raising public awareness about the importance of conservation efforts. Through educational programs, outreach activities, and engaging with tourists, the patrol promotes a deeper understanding of the fragility of the puffin population and the Westman Islands’ ecosystem. This fosters a culture of respect for nature, encouraging responsible behavior and sustainable practices among visitors and locals alike.
Educational materials and interactive displays effectively disseminate knowledge about conservation efforts.
Impact on Tourism and Local Economy
The Puffling Patrol has become a significant attraction for tourists. The opportunity to observe puffins in their natural habitat, combined with the educational aspect of the patrol’s activities, has drawn more visitors to the Westman Islands. This increased tourism has a direct impact on the local economy, stimulating businesses, creating employment opportunities, and generating revenue for the community. The increased visibility of the puffin population, fostered by the patrol, boosts the islands’ reputation as a premier destination for birdwatching and nature enthusiasts.
Comparison of Bird Population Before and After the Puffling Patrol
| Bird Species | Population Before Puffling Patrol | Population After Puffling Patrol | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atlantic Puffin | 1,500 | 1,800 | 20% |
This table presents a simplified example of the impact the Puffling Patrol has had on the Atlantic puffin population in the Westman Islands. While real data might include more variables and species, it demonstrates the potential for population growth and the positive effect of the patrol’s intervention. Significant improvements are often seen across the ecosystem as a whole.
Threats to Pufflings
The delicate lives of pufflings in the Westman Islands are threatened by a complex interplay of natural and human-induced factors. Understanding these threats is crucial for the Puffling Patrol to effectively safeguard these vulnerable birds and ensure the long-term health of the island’s ecosystem. Protecting the puffling population is essential for maintaining the balance of the Westman Islands’ fragile environment.
Primary Threats to Puffling Survival
The Westman Islands’ pufflings face numerous challenges during their critical first few weeks of life. Predators, both natural and human-influenced, pose significant risks. Environmental changes and human activities further complicate their survival.
Impact of Human Activity
Human presence in the Westman Islands, while often well-intentioned, can negatively affect pufflings. Disturbance from tourists, especially near nesting areas, can cause parents to abandon their nests, leaving the young vulnerable. Improper waste disposal can contaminate the environment, affecting the food supply of the pufflings and their parents. Unregulated fishing practices can lead to a decline in the puffling’s food source, disrupting the delicate food web.
Natural Threats to Pufflings
Natural threats to pufflings include predation by larger birds of prey, such as gulls and eagles. Adverse weather conditions, like storms and heavy rain, can damage nests and endanger young pufflings. Disease outbreaks can also decimate puffling populations. These natural threats are an inherent part of the puffling’s environment and require the Puffling Patrol to adapt and respond effectively.
Consequences of Ignoring These Threats
Ignoring the threats to pufflings can lead to a dramatic decline in the Westman Islands’ puffling population. This decline would have cascading effects on the ecosystem. The loss of pufflings would impact the balance of the food chain, potentially affecting other bird species and marine life. The Westman Islands’ unique ecosystem, with its dependence on pufflings, would be severely jeopardized.
Catching a glimpse of the puffling patrol in the Westman Islands is a must-do. Packing snacks and drinks for the day requires a reliable cooler, and for ultimate convenience, check out the best coolers with wheels. These will make transporting your provisions a breeze, ensuring you can fully enjoy the adorable pufflings without worrying about your picnic supplies.
You’ll want to be prepared for the day’s adventures with the puffling patrol!
Puffling Patrol’s Mitigation Strategies
The Puffling Patrol actively addresses these threats through various strategies. These strategies include educating tourists about the importance of maintaining a safe distance from nesting areas. They work with local communities to implement waste management programs. The patrol also monitors fishing practices to ensure sustainability and maintain the puffling’s food source. They actively monitor nesting sites for predators and take necessary steps to protect the pufflings.
Summary Table of Threats and Mitigation Strategies
| Threat | Cause | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Predation by larger birds | Natural predator presence | Monitoring nesting sites, deterring predators (e.g., using scarecrows), and implementing protective measures around nests. |
| Human disturbance | Tourist activity near nesting sites | Educating tourists about the importance of maintaining a safe distance from nesting areas, implementing buffer zones around nesting sites. |
| Waste contamination | Improper waste disposal | Implementing waste management programs, educating local communities, and ensuring proper waste disposal infrastructure. |
| Unregulated fishing | Unsustainable fishing practices | Monitoring fishing practices, promoting sustainable fishing methods, and working with fishing communities to ensure the pufflings’ food supply is not affected. |
| Adverse weather | Storms, heavy rain | Monitoring weather patterns, providing support for nests during high-risk periods, and potentially implementing preventative measures where possible. |
| Disease | Outbreaks of diseases | Monitoring puffling health, implementing early detection programs, and working with veterinary experts to develop preventative measures. |
Puffling Patrol and Conservation
The Puffling Patrol, more than just a heartwarming spectacle, is a vital component of conservation efforts in the Westman Islands. Dedicated volunteers work tirelessly to protect these vulnerable pufflings, directly contributing to the long-term health and survival of the island’s unique ecosystem. Their commitment extends beyond immediate observation, encompassing education and advocacy, ultimately shaping a future where pufflings and the entire island’s biodiversity thrive.The Westman Islands’ remarkable biodiversity is intricately linked to the success of the puffling population.
Puffins, and the entire ecosystem they support, play a critical role in maintaining the delicate balance of the island’s environment. Protecting the puffling population directly impacts the health of the entire island’s food web, from fish populations to the larger predator species. Conservation efforts are not merely about saving a species; they are about safeguarding the interconnectedness of life in this unique environment.
The Puffling Patrol’s Contribution to Conservation, Puffling patrol westman islands
The Puffling Patrol acts as a crucial link between conservation science and the public. By directly monitoring puffling populations and documenting their well-being, the Patrol provides valuable data for researchers. This data, coupled with anecdotal observations, allows scientists to understand and respond to any emerging threats or changes in the puffling population’s health. This hands-on approach fosters a deeper understanding of the local environment and the challenges faced by these fascinating birds.
Ever wanted to witness the adorable puffling patrol of the Westman Islands? It’s a truly special experience, but if you’re looking for a bit more cultural exploration, then checking out the top things to do in Armenia, like the ancient churches and stunning landscapes, could be right up your alley. top things to do in armenia offers some fantastic suggestions.
Regardless of your choice, both puffling patrol and Armenian adventures offer unique and memorable travel experiences.
Significance of Conservation Efforts for Westman Islands’ Biodiversity
The Westman Islands, with their unique geographical features and isolation, harbor a rich tapestry of endemic species. The puffling population, a cornerstone of this biodiversity, directly influences the balance of the island’s ecosystem. A healthy puffling population translates to a healthy marine ecosystem, impacting fish stocks and ultimately supporting a variety of other species. Conservation efforts directly protect the islands’ biodiversity, preserving its unique identity and ecological integrity for future generations.
Role of the Puffling Patrol in Public Education
The Puffling Patrol actively engages with the local community and visitors, providing educational opportunities. These initiatives, through interactive displays, presentations, and guided tours, foster a sense of responsibility and stewardship towards the pufflings and the broader ecosystem. Public awareness campaigns raise crucial funds for ongoing conservation projects. This educational approach cultivates a generation of environmentally conscious individuals who understand the importance of protecting the Westman Islands’ unique biodiversity.
Long-Term Vision for the Puffling Patrol in Supporting Conservation
The Puffling Patrol envisions a future where its activities contribute to long-term conservation strategies. This involves collaborating with scientific researchers, policy makers, and local communities. Continued data collection and analysis, coupled with innovative approaches to conservation, will form the bedrock of their long-term commitment. Their goal is to be more than just a seasonal activity, but a sustainable, impactful program, capable of adapting to future challenges and fostering a lasting legacy of conservation in the Westman Islands.
Conservation Initiatives Undertaken by the Puffling Patrol
- Data Collection and Analysis: The Puffling Patrol meticulously records vital statistics of pufflings, including growth rates, survival rates, and breeding success. This data is invaluable for understanding population trends and identifying any potential threats. For instance, detailed records have helped identify a correlation between pollution levels and reduced chick survival rates.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Through educational workshops, presentations, and online materials, the Patrol informs the public about the importance of puffling conservation. They highlight the role of local communities in protecting the environment, and provide practical steps individuals can take to minimize their environmental footprint.
- Collaboration with Researchers: The Puffling Patrol actively collaborates with marine biologists and ornithologists, sharing collected data and insights. This collaboration ensures that research efforts are aligned with conservation priorities, leading to more effective strategies.
| Conservation Initiative | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Detailed monitoring of puffling populations. | Provides valuable data for researchers to understand population trends and threats. |
| Public Awareness | Educational workshops, presentations, and online materials. | Fosters environmental awareness and community involvement. |
| Collaboration | Partnership with researchers and policymakers. | Ensures that conservation efforts are aligned with scientific knowledge and policy goals. |
Visual Representation of Puffling Patrol

The Puffling Patrol in the Westman Islands needs a strong visual identity to effectively communicate its mission and impact. A well-designed graphic will help raise awareness, inspire volunteers, and foster a sense of community around the crucial work of protecting these vulnerable pufflings. A visual representation should immediately convey the essence of the patrol’s activities and the vital role it plays in conservation.Visuals are crucial in capturing attention and conveying complex information quickly.
A compelling image will not only showcase the patrol’s activities but also evoke the emotional connection necessary to inspire support and action. The design should resonate with the target audience, including potential volunteers, local residents, and tourists.
Ideal Visual Representation
The ideal visual representation of the Puffling Patrol should be a vibrant graphic that evokes a sense of action and protection. It should be dynamic, conveying the patrol’s dedication to safeguarding puffling colonies. The graphic should highlight the patrol’s activities, such as monitoring nests, educating visitors, and collaborating with local communities. The image should be visually appealing and easily understood by a wide audience.
Key Elements of the Visual
The visual should incorporate key elements that represent the essence of the Puffling Patrol. These elements include:
- Pufflings: Depict a diverse range of pufflings in various stages of development, from newly hatched chicks to fledglings, to emphasize the range of ages and life stages protected by the patrol.
- Patrol Members: Show members actively monitoring nests, interacting with visitors, or participating in educational activities, demonstrating their dedication and the collective effort involved.
- Westman Islands Scenery: The background should incorporate iconic imagery of the Westman Islands, such as cliffs, the sea, or nesting sites. This will reinforce the location and the environment the patrol protects.
- Educational Elements: Subtle visual cues, such as an educational pamphlet or a sign, can be included to suggest the patrol’s commitment to environmental awareness and knowledge sharing.
- Color Palette: A vibrant, natural color palette, incorporating blues, greens, and earthy tones, should be used to evoke the natural beauty of the Westman Islands and the life cycle of pufflings.
Possible Visual Representations
This table Artikels potential styles for the visual representation, considering the desired message and target audience.
| Visual Style | Color Palette | Size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Illustration | Vibrant, natural colors (blues, greens, browns) | Large (e.g., 1080 x 1920 pixels) | A lively illustration showcasing pufflings, patrol members, and the Westman Islands landscape, emphasizing action and community. |
| Photographic Montage | Natural, muted tones | Medium (e.g., 800 x 600 pixels) | A visually engaging montage of photographs showcasing various aspects of the patrol’s activities, such as nest monitoring, education, and collaboration with local communities. |
| Symbolic Graphic | Strong, contrasting colors | Large (e.g., 1080 x 1920 pixels) | A graphic featuring symbolic elements like a protective wing, a nest, or a puffling, conveying the patrol’s mission in a concise and powerful way. |
Desired Message
The visual representation should convey the mission and impact of the Puffling Patrol by showcasing the vital role of conservation in protecting pufflings and their habitats. The image should inspire a sense of responsibility and encourage support for the patrol’s efforts. It should clearly demonstrate the interconnectedness between the patrol’s activities and the overall well-being of the puffling population and the Westman Islands ecosystem.
Closure
The Puffling Patrol Westman Islands exemplifies the power of dedicated conservation efforts. Their meticulous monitoring, active protection, and community outreach have created a tangible impact on the islands’ ecosystem. The patrol’s success serves as a beacon for other conservation initiatives, showcasing how human intervention can positively influence biodiversity and foster a harmonious relationship between nature and human presence.
The patrol’s future looks bright as their commitment to the well-being of the pufflings and the Westman Islands’ environment continues.