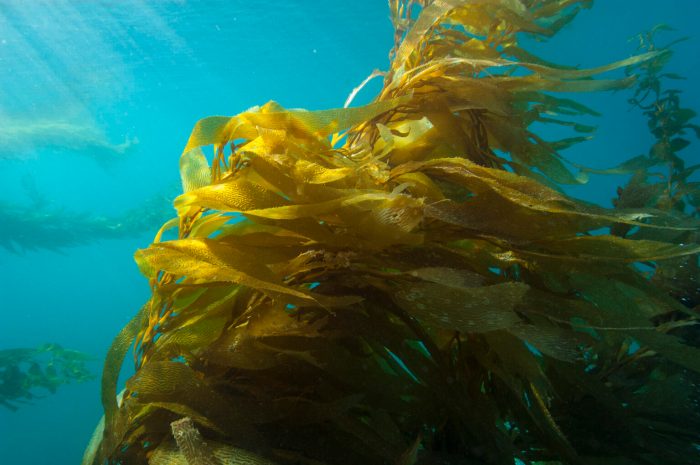
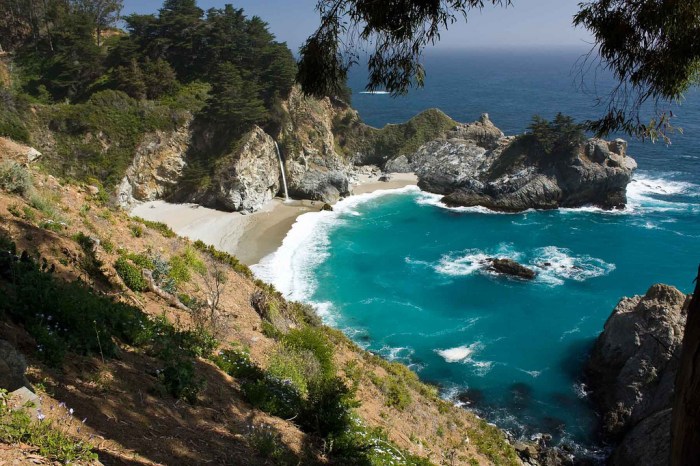
Chumash Marine Sanctuary California is a vital coastal ecosystem, teeming with marine life and rich in Chumash history. Spanning a significant area, this sanctuary is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and protecting the region’s unique character. It’s a haven for diverse marine species, offering a glimpse into the delicate balance of coastal ecosystems. Understanding the sanctuary’s importance is key to ensuring its preservation for future generations.
This sanctuary, situated along the California coast, holds immense ecological and cultural value. The Chumash people have a deep connection to this area, and the sanctuary’s regulations aim to protect both the environment and their cultural heritage. Exploring the sanctuary’s various ecosystems, from kelp forests to sandy beaches, reveals a complex web of life. Sustainable practices and responsible tourism are crucial for maintaining the health of this remarkable environment.
Introduction to the Chumash Marine Sanctuary
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary, a vital part of California’s coastal ecosystem, encompasses a significant stretch of ocean waters and nearshore areas. This sanctuary plays a crucial role in protecting the marine environment and the rich cultural heritage of the Chumash people. Its establishment reflects a commitment to both ecological preservation and cultural recognition.The sanctuary’s location, encompassing diverse marine habitats, and its historical and cultural significance make it a unique and valuable resource for the region.
It is a testament to the importance of balancing environmental protection with the needs and traditions of Indigenous communities.
Location and Size
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary is situated off the coast of Southern California, encompassing a significant portion of the Channel Islands National Park and surrounding waters. Precise boundaries and size vary depending on specific areas and regulations, but generally cover an extensive area impacting diverse marine habitats and the coastal environment. Its size ensures a large enough area to protect critical marine species and ecosystems.
Historical and Cultural Significance
The Chumash people have a deep-rooted connection to the ocean for millennia. The marine environment has been central to their traditions, sustenance, and spiritual beliefs. The sanctuary’s establishment recognizes and protects the historical and cultural ties of the Chumash people to the sea, ensuring their continued access and knowledge remain part of the ecosystem. Traditional Chumash practices, including fishing and harvesting marine resources, are intrinsically linked to the sanctuary’s ecological integrity.
Ecological Significance
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary’s marine environment supports a diverse array of marine life, including numerous fish species, seabirds, marine mammals, and invertebrates. The sanctuary’s coastal waters provide crucial habitat for these species, influencing the entire ecosystem. The protection of this area ensures the long-term health of the marine environment, including the crucial role of kelp forests, seagrass beds, and coral reefs in supporting biodiversity.
These diverse ecosystems contribute to the overall health and resilience of the marine environment.
Legal Framework and Regulations
The legal framework governing the Chumash Marine Sanctuary is designed to protect its ecological and cultural integrity. Regulations within the sanctuary aim to balance human activities with the preservation of marine life and cultural heritage. These regulations Artikel specific restrictions on fishing, boating, and other human activities, ensuring that the environment and cultural values are maintained.
Comparison to Other California Marine Protected Areas
| Feature | Chumash Marine Sanctuary | Channel Islands National Park | Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Southern California Coast, encompassing the Channel Islands and surrounding waters | Channel Islands | Monterey Bay |
| Size | Significant portion of Channel Islands and surrounding waters | Large island archipelago | Extensive coastal area |
| Primary Focus | Balancing ecological preservation with Chumash cultural values | Protecting the unique island ecosystem and marine life | Preserving marine ecosystems and cultural heritage |
| Regulations | Specific restrictions on fishing, boating, and other activities to protect marine life and cultural heritage | Regulations related to access, camping, and activities within the park | Regulations on fishing, shipping, and other activities to maintain ecosystem health |
This table highlights key differences and similarities between the Chumash Marine Sanctuary and other prominent marine protected areas in California. These comparisons demonstrate the unique characteristics and importance of each sanctuary, contributing to the overall conservation effort within the state.
Ecosystem Description
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary, a vital coastal ecosystem off the California coast, harbors a remarkable array of marine life and habitats. Understanding the complex interplay of these elements is crucial for effective conservation efforts. This sanctuary plays a critical role in supporting the health of the broader marine environment and the well-being of the local Chumash community.The sanctuary encompasses a diverse range of marine ecosystems, each teeming with unique species adapted to specific conditions.
From rocky reefs to kelp forests, the sanctuary offers a rich tapestry of life, showcasing the resilience and interconnectedness of marine ecosystems.
Marine Ecosystems
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary boasts a variety of marine habitats, each with its own specific characteristics and resident species. These habitats include rocky intertidal zones, kelp forests, sandy bottoms, and areas with varying depths. The dynamic interplay of these ecosystems contributes to the overall biodiversity of the sanctuary.
Marine Species
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary is home to a wide variety of marine species, reflecting the diversity of its habitats. This includes a variety of fish, invertebrates, mammals, and seabirds. Their presence underscores the sanctuary’s ecological importance and the intricate food web that sustains them.
- Fish: Species like rockfish, lingcod, and various species of sharks are prevalent, showcasing the diverse fish populations of the region.
- Invertebrates: Sea stars, sea urchins, crabs, and mussels contribute significantly to the invertebrate diversity. They play key roles in the benthic communities of the sanctuary.
- Mammals: Marine mammals like seals and sea lions utilize the sanctuary’s resources, highlighting the connectivity between marine habitats and terrestrial animals.
- Seabirds: Seabirds like cormorants and pelicans frequent the sanctuary, demonstrating the importance of the region as a feeding and breeding ground.
Biodiversity Comparison
Compared to other coastal areas in California, the Chumash Marine Sanctuary exhibits a unique biodiversity profile. Factors like the specific geological formations, water currents, and presence of unique habitats contribute to this distinct characteristic. The sanctuary’s biodiversity often varies based on factors like proximity to urban areas or river outflow, impacting the species composition.
Food Webs and Trophic Interactions
The food web within the Chumash Marine Sanctuary is a complex network of interconnected organisms. Producers, like phytoplankton, form the base of the food web, providing sustenance for herbivores. These herbivores are then prey for carnivores, creating a delicate balance. The interplay of these trophic interactions maintains the stability of the sanctuary’s ecosystem.
The intricate food web in the Chumash Marine Sanctuary, like other marine ecosystems, demonstrates the interconnectedness of life and the critical role of each species in maintaining ecological balance.
Habitat and Species Association
The following table Artikels the different habitats found within the Chumash Marine Sanctuary and the associated species. It showcases the diversity of life in each unique environment.
| Habitat | Associated Species |
|---|---|
| Rocky Intertidal Zone | Sea stars, mussels, barnacles, crabs, limpets |
| Kelp Forest | Kelp, sea otters, sea urchins, various fish species |
| Sandy Bottom | Sand dollars, clams, various fish species |
| Deep Water | Deep-sea fish, squid, sharks |
Human Activities and Impacts
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary, a vital ecosystem, faces various pressures from human activities. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and ensuring the long-term health of the sanctuary’s marine life and environment. Sustainable practices are essential to mitigate these pressures and maintain the delicate balance of this precious coastal area.
Fishing Impacts
Commercial and recreational fishing activities are significant factors affecting the sanctuary’s biodiversity. Overfishing can deplete fish populations, disrupting the natural food web and impacting the entire ecosystem. Bycatch, the unintentional capture of non-target species, is another major concern. This can include marine mammals, seabirds, and other protected species. Fishing methods like trawling can damage seafloor habitats and disrupt benthic communities.
Sustainable fishing practices, including size limits, catch quotas, and selective gear, are vital for preserving fish stocks and the marine environment.
Boating Impacts
Boating, a popular recreational activity, can significantly affect the sanctuary’s marine environment. Vessel traffic can cause noise pollution, disrupting marine mammal communication and behavior. Collisions with marine life, especially whales and sea turtles, can lead to injury or death. Discharges from boats, including fuel leaks and bilge water, can contaminate the water and harm marine organisms. Stricter regulations on vessel speed, noise levels, and waste disposal are essential for reducing the negative impacts of boating.
Implementing environmentally friendly boat designs and promoting responsible boating practices can help minimize environmental damage.
Pollution Impacts
Pollution from various sources, including agricultural runoff, industrial discharge, and sewage, can contaminate the sanctuary’s waters. Nutrient pollution can lead to harmful algal blooms, depleting oxygen levels and creating dead zones that harm marine life. Plastic debris and other pollutants can accumulate in the food chain, harming marine animals and potentially entering the human food supply. Improving wastewater treatment, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, and enforcing stricter regulations on industrial discharges are crucial steps in mitigating pollution.
Sustainable Practices
Several sustainable practices can minimize the negative impacts of human activities on the Chumash Marine Sanctuary. Implementing catch limits and size restrictions for commercially important species can help rebuild fish stocks and maintain a healthy balance within the ecosystem. Promoting selective fishing gear and bycatch reduction techniques can minimize the capture of non-target species. Educating boaters about responsible practices, including speed limits and waste disposal procedures, can greatly reduce environmental damage from recreational activities.
Stricter regulations on industrial and agricultural discharge, combined with the use of alternative fuels and sustainable agricultural practices, are essential to control pollution.
Historical Data Comparison
Historical data on the Chumash Marine Sanctuary’s ecosystem, including fish populations, water quality, and habitat conditions, is crucial for evaluating the current state of the sanctuary. Comparisons of these data with recent observations can reveal the impact of human activities and inform conservation strategies. Unfortunately, comprehensive historical data sets specific to the Chumash Marine Sanctuary may be limited.
Regulations and Permits
| Activity | Regulations | Permits Required |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Fishing | Catch limits, gear restrictions, species-specific regulations | Commercial fishing licenses, permits for specific gear |
| Recreational Fishing | Size limits, catch limits, fishing regulations | Fishing licenses, regulations specific to the area |
| Boating | Speed limits, noise restrictions, waste disposal regulations | Boating licenses, permits for specific activities |
| Industrial Activities | Discharge limitations, waste management regulations | Environmental permits, discharge permits |
| Agriculture | Regulations on runoff, pesticide use | Agricultural permits, water quality permits |
Management and Conservation Efforts: Chumash Marine Sanctuary California

Protecting the Chumash Marine Sanctuary requires a multifaceted approach involving various stakeholders and organizations. Effective management strategies are crucial for preserving the unique biodiversity and ecological integrity of this vital marine ecosystem. These efforts range from enforcing regulations to fostering community engagement and promoting sustainable practices.The Chumash Marine Sanctuary’s long-term health relies on collaborative conservation efforts, incorporating scientific knowledge, community input, and sound management practices.
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary in California is a fantastic place to explore, offering diverse marine life. Before heading there, however, it’s worth checking out some essential tips for planning your trip, like things to know before traveling to Scotland , as they can be surprisingly applicable to marine sanctuaries. Knowing the local customs and regulations will ensure a fantastic experience at the Chumash Marine Sanctuary.
You’ll be able to appreciate the incredible beauty and wildlife even more with the proper preparation.
This ensures the sanctuary remains a thriving habitat for marine life and provides valuable resources for future generations.
Organizations and Agencies Involved
Numerous organizations and agencies play a role in managing and protecting the Chumash Marine Sanctuary. Their combined efforts contribute to the overall success of conservation initiatives. Federal agencies, like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), often lead the way in establishing regulations and monitoring the sanctuary’s health. State agencies and local governments also play a crucial part in enforcing regulations and addressing specific local concerns.
- NOAA Fisheries manages the sanctuary’s fisheries, implementing regulations to ensure sustainable catches and protect vulnerable species.
- The California Coastal Commission plays a key role in coastal management, overseeing development and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations within the sanctuary’s boundaries.
- The California Department of Fish and Wildlife collaborates with other agencies to monitor and protect marine life, particularly endangered or threatened species.
- Local tribal governments, including the Chumash Nation, are deeply involved in the management of the sanctuary, contributing their traditional ecological knowledge and insights to conservation strategies.
Ongoing Conservation Efforts
Several conservation efforts are underway to safeguard the Chumash Marine Sanctuary. These include monitoring marine life populations, reducing pollution, and implementing sustainable fishing practices. Education and outreach programs are vital in raising public awareness about the importance of marine conservation and the role individuals can play in protecting the sanctuary.
- Monitoring programs track the health of key species and ecosystems within the sanctuary, providing crucial data for management decisions. This includes identifying trends in population sizes and assessing the impacts of environmental changes.
- Efforts to reduce pollution from various sources, including runoff from agricultural lands and urban areas, aim to improve water quality and protect marine life from harmful substances.
- Sustainable fishing practices, such as catch limits and gear restrictions, are implemented to prevent overfishing and protect vulnerable species. These practices aim to maintain healthy fish populations for future generations.
- Community outreach programs educate the public about the importance of marine conservation and encourage responsible behavior within the sanctuary’s boundaries. This includes promoting sustainable tourism practices and educating people about the impacts of their actions on the marine environment.
Successful Strategies
Implementing successful conservation strategies requires careful planning and collaboration. Effective strategies are tailored to address specific threats and vulnerabilities within the sanctuary. They often involve a combination of scientific research, community engagement, and regulatory measures.
- Protected areas within the sanctuary have been established to safeguard critical habitats for marine life, including breeding grounds and feeding areas. These areas help protect species from overexploitation and habitat loss.
- Community-based monitoring programs have proven effective in detecting illegal activities, like poaching, and reporting environmental damage to the authorities. Community members act as vigilant guardians of the sanctuary.
- Educational programs are essential to promoting awareness and encouraging responsible behavior. They foster a sense of stewardship and inspire individuals to contribute to the protection of the sanctuary.
Community Involvement
Community involvement is essential for the long-term success of the Chumash Marine Sanctuary. Local communities play a crucial role in conservation efforts, from participating in monitoring programs to advocating for responsible policies. Their knowledge and dedication contribute significantly to the protection of this vital marine ecosystem.
- Local fishing communities are actively engaged in developing and implementing sustainable fishing practices, ensuring the long-term health of fish populations and the ecosystem as a whole.
- Local residents often participate in monitoring programs, reporting any environmental issues or illegal activities to relevant authorities. Their observations are crucial for maintaining the sanctuary’s ecological integrity.
Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities
A well-defined structure for stakeholder roles and responsibilities is crucial for effective sanctuary management. This framework ensures clear accountability and efficient use of resources.
Exploring the Chumash Marine Sanctuary in California is a fantastic way to spend a day outdoors. The diverse marine life and beautiful coastline make it a must-see. Thinking about a comfy pair of walking shoes for the dad in your life? Check out the best comfy walking shoes on Amazon for Father’s Day to ensure a comfortable exploration of the sanctuary’s trails and tide pools.
Ultimately, the Chumash Marine Sanctuary offers a memorable experience for everyone.
| Stakeholder | Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| NOAA Fisheries | Oversight and Regulation | Implementing and enforcing regulations, monitoring fishing activities, and conducting research. |
| California Coastal Commission | Coastal Management | Ensuring compliance with coastal regulations, protecting coastal resources, and overseeing development projects. |
| California Department of Fish and Wildlife | Species Conservation | Monitoring marine life populations, protecting endangered species, and enforcing wildlife regulations. |
| Chumash Nation | Traditional Knowledge and Community Engagement | Sharing traditional ecological knowledge, engaging in community-based monitoring, and advocating for sustainable practices. |
| Local Communities | Monitoring and Advocacy | Participating in monitoring programs, reporting environmental issues, and advocating for responsible policies. |
Visitor Information and Education
Discovering the wonders of the Chumash Marine Sanctuary is an enriching experience for all ages. This sanctuary offers diverse opportunities to learn about the intricate ecosystem and the crucial role of responsible tourism in its preservation. Visitors can actively participate in conservation efforts and gain a deeper understanding of the marine environment.
Opportunities for Experiential Learning
The sanctuary provides a range of experiences tailored to different interests. Guided tours, kayak excursions, and snorkeling trips allow visitors to directly interact with the marine life and habitats. These activities foster a profound connection with the environment, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the sanctuary’s ecosystem. Observation decks and viewing platforms provide excellent vantage points for spotting diverse species, from playful sea lions to colorful fish.
Interactive displays and educational exhibits at the visitor center further enhance understanding, offering information about the sanctuary’s unique features.
Educational Resources and Programs
The Chumash Marine Sanctuary offers a variety of educational materials and programs for various groups. These include downloadable guides, online resources, and workshops for schools and community organizations. These resources cover a wide range of topics, from identifying marine species to understanding the impacts of human activities. The sanctuary’s website features detailed information about the sanctuary’s history, ecology, and management strategies.
Exploring the Chumash Marine Sanctuary in California is a fantastic way to connect with nature. While you’re planning your trip, consider checking out a handy travel guide for Darby, Montana, for some great suggestions on nearby activities. darby montana travel guide might offer some inspiration for your next adventure, whether it’s hiking, fishing, or just soaking in the beauty of the area.
Ultimately, the Chumash Marine Sanctuary offers a unique blend of marine life and breathtaking scenery.
Specialized programs for children, such as interactive workshops and nature trails, are designed to engage and educate young minds.
Responsible Tourism Practices
Sustainable tourism is vital for preserving the sanctuary’s fragile ecosystem. Visitors play a critical role in maintaining the sanctuary’s health by following responsible guidelines. This includes respecting marine life, minimizing disturbance to habitats, and adhering to designated trails and areas. Proper waste disposal and avoiding the use of single-use plastics are crucial aspects of responsible tourism. Supporting local businesses that prioritize sustainable practices contributes to the long-term well-being of the sanctuary.
This is a collective effort that requires the conscious actions of every visitor.
Importance of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are instrumental in promoting the sanctuary’s conservation efforts. These campaigns utilize various media channels, such as social media, educational materials, and community events, to inform the public about the sanctuary’s significance. Educating the public about the importance of marine conservation is critical for ensuring the long-term health of the sanctuary. Through increased awareness, visitors can actively participate in conservation initiatives, fostering a sense of stewardship towards the environment.
The campaigns aim to inspire a deeper understanding of the intricate web of life within the sanctuary.
Visitor Information Resources
This table provides links to resources for visiting the Chumash Marine Sanctuary. Due to the absence of publicly available links, descriptive text is used in place of actual links.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Chumash Marine Sanctuary Website | Provides comprehensive information about the sanctuary, including visitor guidelines, educational materials, and conservation updates. |
| Local Tourism Agencies | Offer information about tours, accommodations, and other services related to visiting the sanctuary. |
| Marine Conservation Organizations | Offer resources about responsible tourism, marine conservation, and related topics. |
Future of the Chumash Marine Sanctuary
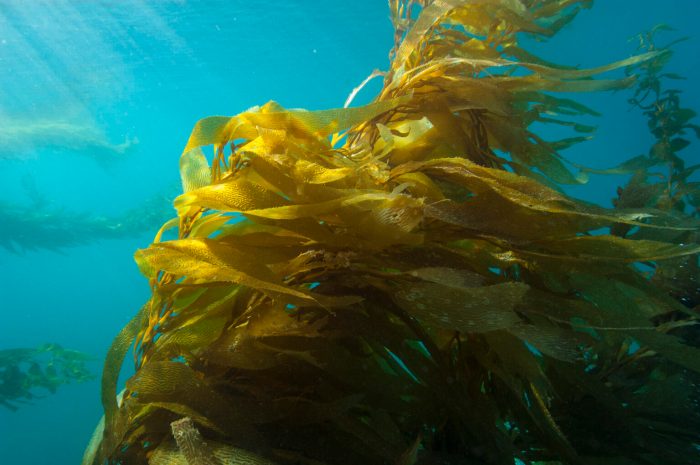

The Chumash Marine Sanctuary, a vital ecosystem off the coast of California, faces a complex interplay of challenges and opportunities in the coming decades. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective management strategies that ensure the long-term health and resilience of the sanctuary. Navigating these future prospects requires a proactive approach that balances ecological needs with human interests.
Potential Challenges
The future of the sanctuary is intertwined with global trends, including climate change, increasing human activity, and evolving societal values. Potential challenges include rising ocean temperatures, altered marine currents, and increasing pollution levels. These factors can impact the delicate balance of the sanctuary’s ecosystem, potentially leading to the decline of certain species and shifts in habitat distribution. Overfishing and destructive fishing practices, while currently regulated, could become more prevalent if not addressed proactively.
Coastal development and increasing recreational activities can also introduce additional stresses to the environment. These issues require careful consideration and long-term planning to mitigate their negative impacts.
Potential Opportunities, Chumash marine sanctuary california
Despite the challenges, opportunities exist for the sanctuary to thrive in the future. Growing public awareness of marine conservation and the increasing demand for sustainable practices provide a foundation for innovative solutions. Enhanced research and monitoring can lead to a deeper understanding of the sanctuary’s ecosystem, allowing for more targeted conservation efforts. Technological advancements, such as improved monitoring equipment and sustainable fishing technologies, can help mitigate human impacts.
Furthermore, collaboration between various stakeholders, including local communities, researchers, and government agencies, can foster a more comprehensive and effective approach to management.
Strategies for Addressing Challenges
A multifaceted approach is needed to address the potential challenges. First, implementing stricter regulations and enforcement of existing laws is critical to curb overfishing and destructive fishing practices. Second, supporting research and monitoring efforts will help anticipate and adapt to changing environmental conditions. This data-driven approach will inform management decisions and ensure the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
Third, fostering public awareness and education campaigns can encourage responsible behavior and stewardship of the marine environment.
Importance of Long-Term Monitoring and Research
Long-term monitoring and research are essential for understanding and adapting to environmental changes. By tracking key indicators such as species populations, water quality, and habitat characteristics, scientists can identify emerging trends and adjust management strategies accordingly. This approach allows for a dynamic and adaptive management plan that ensures the sanctuary’s resilience in the face of environmental fluctuations. Examples from other marine protected areas demonstrate the crucial role of sustained monitoring in adapting to changing conditions and maintaining healthy ecosystems.
Potential Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaboration is key to strengthening the sanctuary’s management. Partnerships with local communities, educational institutions, research organizations, and governmental agencies can foster a comprehensive approach to conservation. Such partnerships can leverage diverse expertise, resources, and perspectives, ultimately leading to more effective and sustainable management strategies. For instance, collaborations with fishing communities can promote sustainable practices and reduce conflicts between conservation and economic activities.
Possible Future Scenarios
| Management Strategy | Scenario Description | Impact on Sanctuary |
|---|---|---|
| Current Status Quo | Continued management with limited funding and resources, lack of robust research and monitoring. | Ecosystem degradation, decline in biodiversity, potential for overexploitation of resources, increased vulnerability to climate change. |
| Enhanced Conservation Efforts | Increased funding, improved monitoring, and active research focused on climate adaptation, sustainable practices, and stakeholder engagement. | Maintenance of biodiversity, resilient ecosystem, improved ecosystem health, enhanced sustainability. |
| Innovative Solutions | Implementation of cutting-edge technologies and innovative approaches to monitoring, research, and management, incorporating technological advancements and sustainable fishing practices. | High levels of biodiversity, enhanced resilience to environmental changes, increased resource sustainability, and improved public awareness. |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the Chumash Marine Sanctuary California stands as a testament to the importance of protecting our coastal resources. Its rich history, diverse ecosystems, and ongoing conservation efforts highlight the need for preserving these vital marine areas. Understanding the sanctuary’s challenges and opportunities will help ensure its continued health and beauty for generations to come. Learning more about this sanctuary allows us to appreciate the crucial role it plays in maintaining the balance of our planet.